CNSC regulatory framework – Fact sheet
The Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) regulates to protect the health, safety and security of Canadians as well as the environment, and to respect Canada's international commitments on the peaceful use of nuclear energy. Established in 2000 under the Nuclear Safety and Control Act (NSCA), the CNSC reports to Parliament through the Minister of Natural Resources. To safely regulate an evolving nuclear sector, the CNSC maintains an effective and flexible regulatory framework.
The NSCA gives the CNSC the power to license, and:
- states that any persons wishing to carry out nuclear-related activities in Canada must first obtain a licence from the CNSC
- authorizes the CNSC to attach any conditions to licences that it deems necessary to meet the NSCA’s requirements
- authorizes the CNSC to make Regulations
What is the CNSC regulatory framework?
The CNSC's regulatory framework consists of laws passed by Parliament that govern the regulation of Canada's nuclear industry, and regulations, licences and documents that the CNSC uses to regulate the industry. These documents fall into two broad categories: those that set out requirements, and those that provide guidance on requirements. The CNSC is committed to providing regulatory tools that achieve clarity of its requirements.
The foundation for the CNSC’s regulatory framework is the Nuclear Safety and Control Act. The NSCA empowers the CNSC to make regulations and to develop other regulatory tools to establish requirements for and provide guidance related to the use of nuclear energy and materials in Canada.
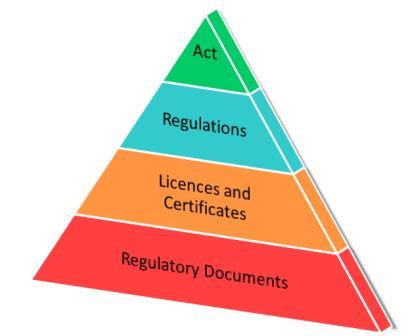
The CNSC’s regulatory framework elements fall into two categories: requirements and guidance.
Requirements are mandatory. Licensees or applicants must meet these requirements to obtain or retain a licence or certificate to use nuclear materials or operate a nuclear facility. Regulatory instruments under requirements include:
- NSCA – The Act to establish the CNSC, with the authority to regulate the nuclear industry.
- Regulations – Sets out statutory requirements.
- Regulatory documents – Provide greater detail than regulations, as to what the licensees and applicants must achieve in order to meet the CNSC’s regulatory requirements.
Guidance provides direction to licensees and applicants on meeting requirements. Regulatory tools under guidance include:
- Guidance documents – Provide practical guidance to licensees and applicants on how to meet the regulatory requirements of the CNSC.
- Staff review procedures – Internal working documents used by CNSC staff to conduct regulatory reviews. Staff review procedures ensure consistent regulatory reviews.
- INFO-documents – Plain-language publications describing nuclear-related issues and regulatory requirements and processes, for the general public and other stakeholders. INFO documents also provide support and further information on other elements of the regulatory framework.
The CNSC’s regulatory framework ensures clear direction to industry, stakeholders and CNSC staff. The CNSC’s primary focus is to create a framework that supports the timely development and publication of regulations, regulatory documents and associated guidance.
Page details
- Date modified: